Market Correlation: How Different Assets Relate
Market correlation: Understanding a complex relationship between cryptocurrency
The world of cryptocurrencies has exploded in recent years, while prices have grown suddenly and have dropped in rapid succession. While some investors are attracted by high yields perceived and the speculative nature of the crypt, others are more cautious and admit that the market is inestable. One of the areas in which the cryptocurrency market has been particularly fascinating is the concept of market correlation – the way in which different assets apply to each other in terms of their price movements.
What is market correlation?
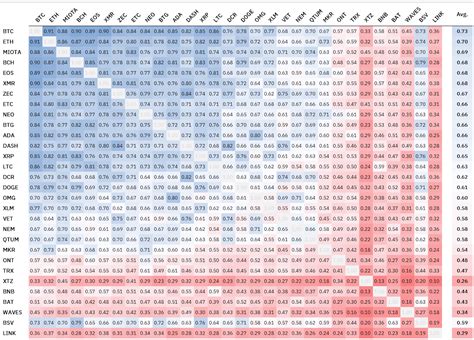
Market correlation is applied to adapt to two or more assets, along with changes on the general market. In other words, they measure how thorough the prices of two or more cryptomas are linked. This concept is decisive, because it helps investors to understand the interconnections of different assets and make the knowledge of the case.
Why does the market correlation matter?
Market correlation is important for several reasons:
- Recognizing these relationships, investors can adjust their strategies to minimize losses and maximize profits.
- Trading strategies
: Market correlation affects the effectiveness of different business strategies, including the next trend, average reversal and statistical arbitration. By identifying correlations between assets, traders can develop more efficient strategies that use market inefficiency.
- Investment decisions : Market correlation plays an important role in investment decisions, especially for institutional investors who have to manage large portfolios. Analyzing the relationships between different assets, these investors can optimize their risk profiles and reach their long -term goals.
Cryptoma Square: Perfect Example
The crypto park is often reported as a demonstrative example of market correlation. The prices of different cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH) and Litecoin (LTC), have a historically correlated. This relationship is supported by several factors:
- As the prices rise suddenly, these investors are more likely to sell their coins, which makes prices fall.
- Additional assets : Some assets in the Crypto marking, such as Altcoins and Stableins, may show mutual complementary relationships. For example, Bitcoin (BTC) often stops well with Ethereum (ETH), while, apart from Litecoin (LTC), they tend to get the bear’s market better.
3 If investors are optimistic about the future of the crypt market, they could be more willing to risk and buy more assets, which leads to an increase in correlations.
Examples of correlated assets
Some examples illustrate the concept of assets correlated on the cryptological market:
1.
- Litecoin (LTC) and Bitcoin (BTC) : As an alternative to Bitcoin Litecoin, it often works well when prices are low or fall, because investors are looking for more stable assets during market decline.
- Crop (xrp) and bitcoin (BTC) : The price of correction was correlated with bitcoins, especially during high volatility.
Conclusion
Market correlation is a powerful tool to understand complex relationships between different cryptocurrencies.

